

- #TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH HOW TO#
- #TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH MAC OS#
- #TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH UPDATE#
- #TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH CODE#
#TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH UPDATE#
If you don't understand what " update the hard-disk accordingly" actually means, you might need to refresh your knowledge of how distribuited source control managers like Mercurial actually work: if that's the case, you should read here for more info.Īs soon as you do that, move to the Extensions section. This way, every time the local repository will be updated with a synchronize/pull operation, Mercurialwill also update the hard-disk version accordingly. Once there, change the value of the Operation to perform after pull dropdown to Update.

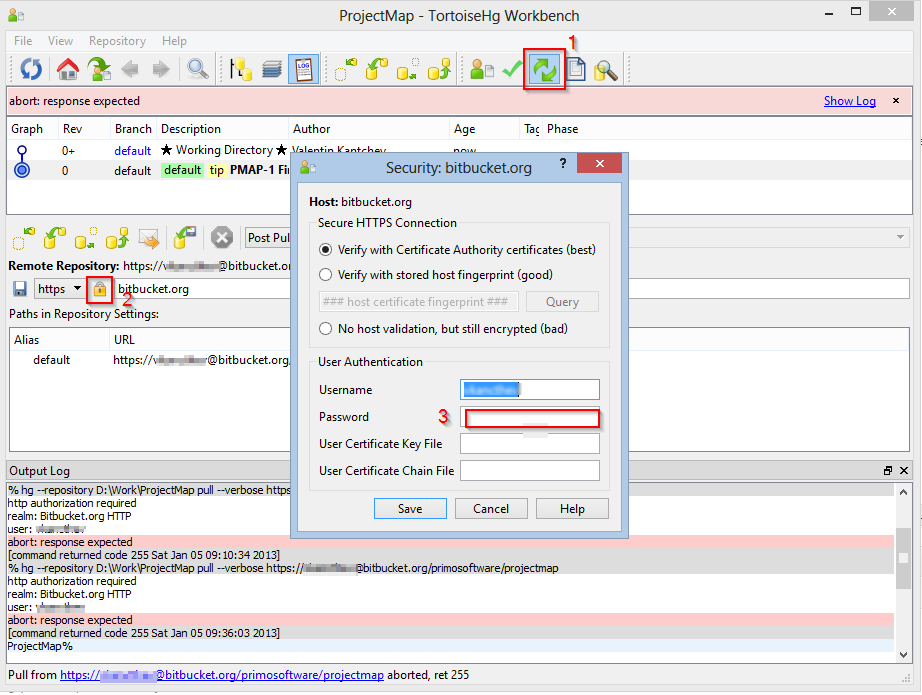
Navigate through the Sync section using the menu to the left. Let's open up the TortoiseHg Workbench, then navigate through File > Settings: the TortoiseHg settings modal window will open. Configuring TortoiseHgīefore digging into Visual Studio 2015 it can be wise to change a couple things to the TortoiseHg 's default settings. On the other hand, whenever we need to change some configuration settings, the TortoiseHg Workbench will be very handy, providing the proper GUI tools to do that: that's precisely what we need to do right now. For example, if you need to Clone an existing project in a matter of seconds, the context menu add-on will most likely be the right choice: all you need to do is right-click on the destination folder, select TortoiseHg > Clone. and enter the repository URL to start the cloning process. Image 2 - TortoiseHg context menu add-onsĮither one of them can be useful, depending on any given scenario. Image 1 - TortoiseHg Workbench main screen
#TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH HOW TO#
In the unlikely chance you never heard about it, we strongly suggest reading its Wiki page and/or pay a visit to its official home page: in this post we'll briefly explain how to properly configure Visual Studio 2015 to effectively use Mercurial as main Scc Manager as a viable replacement (or worthy companion) to GIT, SVN or even the more-than-deprecated Visual SourceSafe.
#TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH CODE#
This is not the first time we're talking about Mercurial, one of the best Distribuited Source Code Control Manager for Windows, also known as HG. A stand-alone alternative: HgSccPackage.Setting VisualHG as default Source Control Manager.

#TORTOISEHG WORKBENCH MAC OS#
The thg script and TortoiseHg dialogs can be used on any platform that supports PyQt, including Mac OS X. TortoiseHg is primarily written in Python and PyQt (the Windows shell extension being the notable exception). TortoiseHg binary packages list Mercurial as a dependency, so it is usually installed for you automatically. You must have Mercurial installed separately in order to run TortoiseHg on Linux. On Linux, TortoiseHg consists of a command line thg script and a Nautilus extension which provides overlays and context menus in your file explorer.
Binary packages of TortoiseHg for Windows come with Mercurial and a merge tool and are thus completely ready for use "Out of the Box". On Windows, TortoiseHg consists of a shell extension, which provides overlay icons and context menus in your file explorer, and a command line program named thg.exe which can launch the TortoiseHg tools. TortoiseHg is a set of graphical tools and a shell extension for the Mercurial distributed revision control system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
